Why Scalability in the Cloud?
Hey friends,
Today, we will learn and understand all about Scaling Applications and Systems in the Cloud.
There are two types of scaling in the cloud: Vertical and Horizontal.
Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling involves increasing the processing power of a single machine. In the diagram, we have an EC2 Server getting bigger, indicating an upgrade in CPU, RAM, or storage resources.
How this works is: Imagine you have a computer server handling web traffic. If the traffic increases and the server needs more power to manage the load, you will upgrade the server's hardware.
This could mean adding more memory, a faster processor, or storage capacity to the existing server.
Vertical scaling is limited because you can only upgrade a machine so much. Eventually, you may reach the maximum capacity that a single machine or instance can handle, and at that point, vertical scaling is no longer an option.
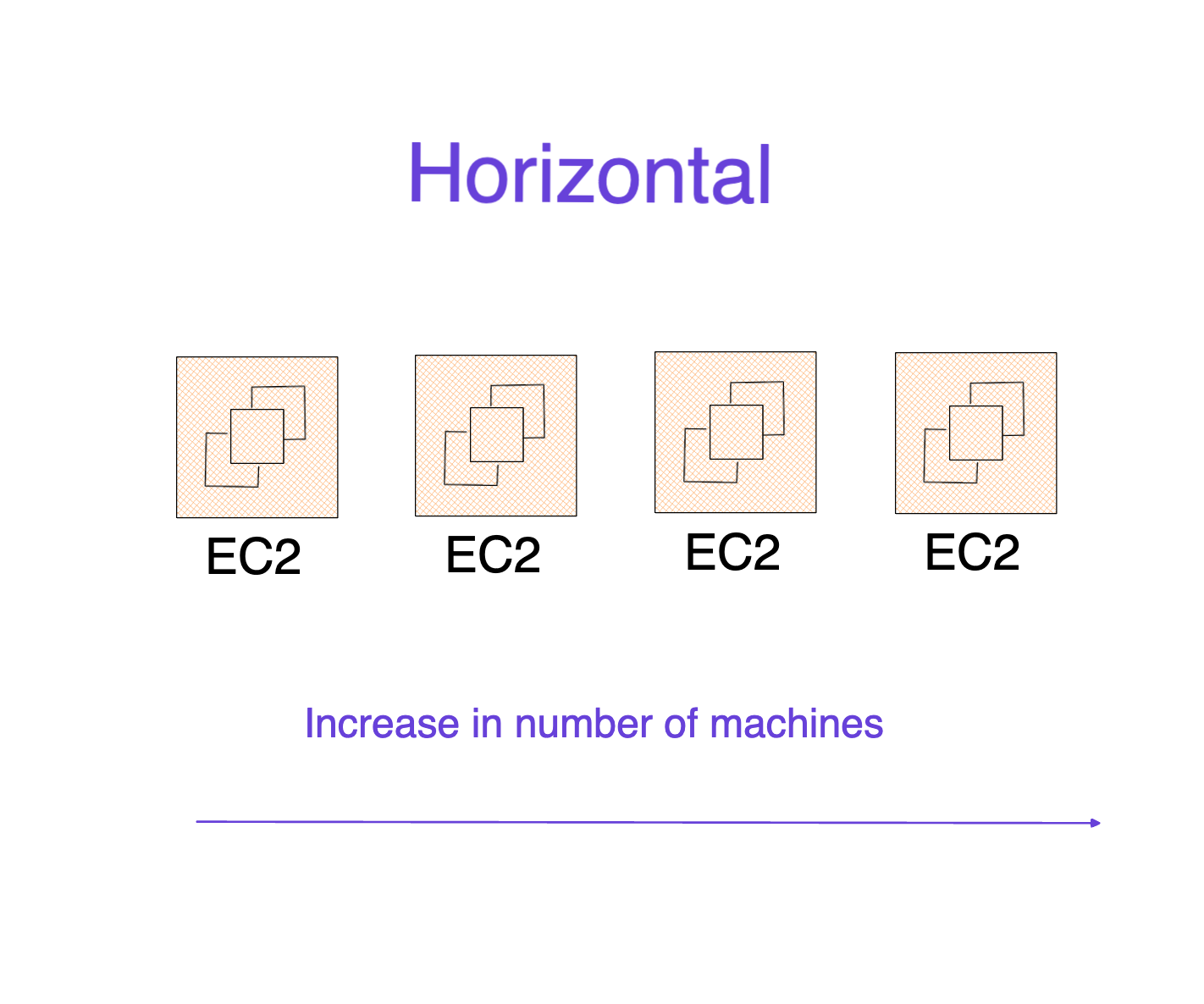
Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal Scaling involves increasing the number of machines in a system. In the diagram, we have the number of EC2 Servers multiplying, indicating adding more servers to handle the load.
How this works is: If more capacity is needed, instead of upgrading the server's hardware, you would add more servers of the same size. Each server shares the workload, distributing the traffic between them.
Horizontal scaling allows for virtually limitless growth by adding more machines as needed. This approach also offers high availability and fault tolerance because if one server fails, the others can pick up the load.
Cloud Engineer Academy Launch
The Cloud Engineer Academy launched last weekend, and our initial students for their hands dirty with Cloud Fundamentals, Git and Cloud Architecture.
Here is some of their feedback:
If you use code “LAUNCH100”, you can get $100 off for being a newsletter subscriber.
As always, Keep working.
Soleyman
📸 My New Videos:
Will an AWS Certifications Get Me a Job in 2024?